SITE LAYOUT SECTION
Section
I BUILDING LAYOUT
OBJECTIVES:
The
objectives of surveying for building construction are to lay out the proposed
structure according to prepared plans and to mark the controlling points of the
structure in the manner that is most useful to the construction forces. This
marking consists of indicating the corners of the building and other horizontal
and vertical positions by means of stakes, batter boards with string lines,
drill holes, cut-and-fill notations, and similar conventional methods.
The actual
layout of the building is usually preceded by some form of reconnaissance and
location survey. The following procedures are typical of major building
projects:
• Performing
reconnaissance (aerial, map, and ground)
• Selecting
site (paper and instrument).
• Establishing
control (horizontal and vertical).
• Taking
topography (plane table or transit stadia).
ORIENTATION
The building
and its foundation are positioned according to the controlling dimensions and
references appearing on prepared plans. The dimensions and references include
the overall length and width of the structure, distances to road center lines
and to other structures, measurements within the structure itself, and
miscellaneous determinations concerning the approaches and rights-of-way.
LAYOUT OF A SIMPLE BUILDING
The plans
for construction of a building give the location and elevation of the work
relative to existing utilities and survey control marks. The dimensions of the
building are part of the necessary data for establishing line and grade. Figure
6-1 illustrates atypical building layout using the following steps.
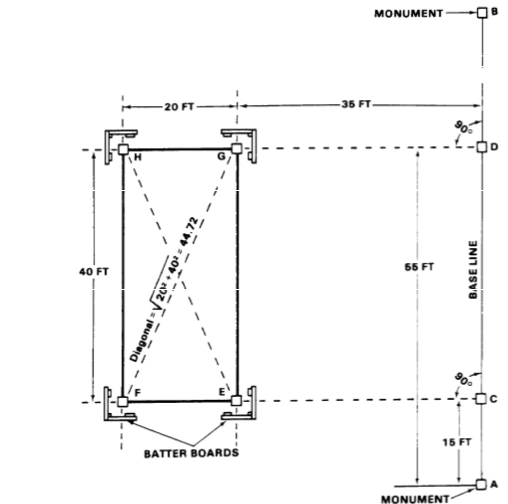
Establish baseline
AB and locate CD by measurement
At point C,
turn 90 degrees from B and locate corner stakes E and F by measurement.
Locate
points H and G from point D in the same way
(1)
(2)
Install batter boards.
(3)
Establish line and grade
BATTER BOARDS
The surveyor
locates the corners of the building and determines the elevation of its foundation
by carrying forward elevations from a benchmark, or other point of known elevation,
to the foundation. To mark the general location, the surveyor sets stakes or
slats. These will guide the initial excavation and rough grading. However, the
stakes will be disturbed or destroyed during this work and somemore suitable
marks must be placed to continue the construction. These suitable marks are
called batter boards. The surveyor uses these temporary devices to mark the outline
and grade of the structure and any special construction inside or outside.
Placement:
Batter
boards of two 2- by 4-inch stakes driven into the ground and a crosspiece of 1-
by 6-inch lumber naled to each stake. The surveyor drives the stakes about 3 to
4 feet away from the building line so they will not be disturbed by the
construction but will be far enough apart to straddle the line to be marked.
Note that in figure 6-2 only three stakes, one of them being a common post for
two directions, are driven on outside corners. The length of the stakes is
determined by the required grade line. They must be long enough to accept the
1- by 6-inch crosspiece to mark the grade. The surveyor cuts the 1- by 6-inch
crosspiece long enough to join both stakes and nails it firmly to them after
the grade has been established. The top of the crosspiece becomes the mark from
which the grade will be measured.
Use of Instrument:
The surveyor
sets all batter boards for one structure to the same grade or level line. An
instrument is used to locate the building lines and mark them on the top edge
of the crosspiece. A nail is driven at each of these marked points. A cord
stretched over the top edge of two batter boards and held against the nails
defines the building line and grade elevation.
Use of Cords:
Sometimes,
an instrument is not available for marking the building line on the batter
boards. If the corner stakes have not been disturbed, the surveyor can transfer
the building line to the batter boards by stretching a cord over the batter
boards and using plumb bobs held over the corner stakes. The surveyor moves the
cord on each batter board until it just touches both plumb bob strings, marks
the position of the cords, and drives in the nails.
Procedures:
The surveyor
sets and marks the batter boards as follows:
After the
corner stakes are laid out, drive
(1) 2- by
4-inch stakes 3 to 4 feet outside of each corner. These are selected to bring
all crosspieces to the same elevation.
(2) The
surveyor marks these stakes at the grade of the top of the foundation or at
some whole number of inches or feet above or below the top of the foundation.
Use a level to mark the same grade or elevation on all stakes.
(3) Nail 1-
by 6-inch boards to the stakes to the top edge of the boards and flush with the
grade marks. Mark the distance in crayon on these boards.
(4) Locate
the prolongation of the building lines on the batter boards by using an
instrument or a line and plumb bob
(5) Drive
nails into the top edges of the batter boards to mark the building line
INTERIOR TRANSFER OF LINE
AND GRADE
Occasionally, it is necessary to transfer lines and grades
from outside to inside a building and to the upper stories for establishing
wall faces, floor levels, and columns or for setting machinery precisely. The
surveyor does this by traversing and leveling.
Location:
The surveyor locates instrument stations outside of the
building to establish a line that, when extended, will intersect the building
at a window or doorway. The instrument is set on the station farthest from the
building and sighted on the point nearest the building. The surveyor transfers
the line to the building by sighting the instrument on a plumb bob held in an
upper-story window.
From this point, the line is extended in any direction inside
the building by setting up on the point and using the outside stations as a back
sight. The line is prolonged by double centering. Because of the short sights
used, the surveyor may accurately set an angle that is to be turned to clear an
obstruction and then measure by repetition.
Direct Leveling:
To transfer vertical control into a building, the surveyor
uses direct leveling, if possible. For elevation transfer to an upper story, a
steel tape is suspended with a weight attached to the lower or zero ends. To
insure accuracy, the weight should approximately equal the normal tension of
the fully supported tape minus one half of the weight of the suspended portion
of the tape. A level is set up on the first floor, and a reading is taken on
the suspended tape.
Another reading is taken on the tape with a level set on the
upper floor. This gives data from which the HI of the instrument on the upper
floor is computed. A rod is now held on some point on the upper floor to be
used as a benchmark and its elevation determined. The surveyor may also
establish elevations on the second floor by using the rod upside down (often
called an inverted rod) and marking the elevation on a wall.
Section
II. UTILITIES LAYOUT
DRAINAGE:
Utilities drainage refers to the sewer systems for surface
water and liquid waste. The design and location of a drainage or storm sewer system
will depend upon the size and topography of the area to be drained, the intensity
of rainfall expected, the runoff characteristics of the area, and the location of
the disposal point. The area to be drained includes the installation and any
area around it that will drain into the installation. The intensity of the
rainfall in inches per hour is based on records of past storms. The runoff
characteristics are determined by the type of soil and ground cover.
DESIGN AND LOCATION:
Using the factors mentioned and the best available
topographic map of the area, the surveyor designs and locates the sewer lines
on paper. Once the paper location is accomplished, the centerline of the ditch
is staked and profile levels run. The profile and grade lines are plotted and
cut stakes set.
After the trench is dug, batter boards are set for the
alignment of pipes and placement of manholes or drop inlets. The surveyor
usually places batter boards for sewer alignment at intervals of 10 to 25 feet
and sets them on edge across the trench (figure 6-3). Then the surveyor
determines the interval between batter boards, the station number, and the
elevation of the sewer grade at each batter board.
The term sewer grade is interchangeable with such other terms
as invert grade, pipe grade, flow line, and grade line elevation. They all mean
the same thing, the elevation of the low point on the inside circumference of
the pipe. All sewer lines are designed with this elevation as the controlling
factor. The surveyor must set all grade marks on the batter boards between two
successive manholes at the same distance above the invert grade.
Battens:
The surveyor nails battens (small pieces of wood) to the
batter boards to indicate sewer alignment. All battens are set vertically on
the same side of the batter boards, with the same edges directly over the
center line of the sewer. As work progresses, the surveyor must check the
alignment of these battens frequently. This is done by sighting past the edges
marking the center line. Any batten that has been moved or disturbed will be
visible immediately.
Sighting Cords:
The surveyor uses a sighting cord stretched parallel to the
center line of the sewer at a uniform distance above the invert grade to
transfer line and grade into the trench. After computing the invert elevation,
the surveyor adds an even number of feet to establish the elevation of the cord
at each batter board. This position is marked on the center line edge of each
batten by a nail. The sighting cord is fastened to the battens at these
nails and this establishes the alignment of the sewer. The center line is
directly below the cord, and the sewer invert grade is at the selected distance
below the cord.
Grade Transfer:
To transfer the grade, usually in
feet or feet and inches, from the sighting cord to the pipe, the surveyor uses
a rod or stick called a grade pole, with a mark at a distance from the foot piece
equal to the distance between the sighting cord and the invert grade (figure
63). The foot piece is placed on the invert of the pipe, and the rod plumb is
held. The pipe end is then raised or lowered until the mark on the grade pole
is on a horizontal line with the cord. A plumb line is held lightly against the
cord and the pipe shifted sideways until its crown is directly below the point
of the plumb bob. The grade pole is again placed in position, held plumb, and
its mark checked against the cord.
THANKS!